What is Carding:
The carding is the second process of spinning department which converts fed material i.e. lap or uniformed lap form material i.e. chute feed system into the uniform strand of fibres called “sliver”. The good quality carding of cotton is very important because the quality of yarn are very much depends upon it. The neps percentage in the yarn varies according to the quality of carding process.
“The carding is called the heart of spinning”.
In the carding process, the material gets passed through a carding machine. The fibres are made parallel to each other. The fibres in this operation, thus it makes it possible to remove all types of impurities present in the cotton.
The carding, stripping and raising action take place during carding operation. In this way, a continuous uniform sliver having a parallel fibre arrangement almost free of impurities is obtained after carding process.
Objects of Carding Machine:
∎ To make the fibres parallel.
∎ To individualize the fibres.
∎ To remove impurities.
∎ To clean cotton thoroughly off the lighter dirt & trash as well as to remove a certain proportion of neps & short fibres from the opened material.
∎ To remove very short fibres that could not be spun into yarn.
∎ To convert Blow Room lap or Chute feed sheet into the loose, roughly parallel, untwisted strand of fibres called ‘sliver’.
Different Zones of Carding Machine:
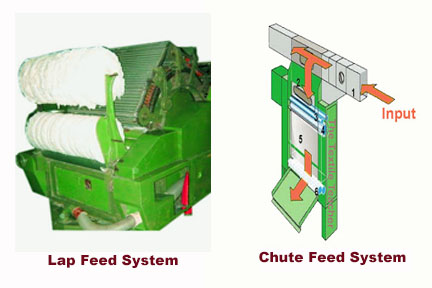
∎ Chute feed/ Lap :
The feed material for carding is in the form of Blow Room lap or by direct Chute feed system, In chute feed system the small tufts of fibres in sheet form fed directly from blow room to a series of cards, arranged in a circuit through pneumatic pipe.
∎ Feed roller & Licker-in:
The roller that receives fibres from the feed roll is called the licker-in. Licker-in opens the cotton into very small tufts, extracting the seed bits, sand and other vegetable trash particles from cotton. Licker-in transfers the cotton to the cylinder zone.

∎ Cylinder & Flats:
The main work of the card is to individualize fibres which is performed between the main cylinder and the flats. Only by means of this fibre separation it is possible to eliminate the dirt, especially the finer particles and dust.

∎ Doffer:
Fibres from cylinder are transferred to doffer. Difference in speed of cylinder and doffer enables fibre to be stripped by stripper roller from doffer to form card web.

∎ Condensation of web & Trumpet:
The fibre web is stripped from the doffer using a stripper roller. It is then passed through a pair of squeeze rolls before it is finally accumulated width wise into a fibre strand form i.e. Card Web. The calendar rolls compress the fibre strand to provide better integrity and stable flow of material. The fibre strand means the card sliver proceeds upward over guide pulleys to enter the coiler system. This consists of a trumpet, guide and the second pair of calendar rolls that delivers the carded sliver through a revolving tube into the card sliver can.

∎ Sliver & Carding Can:
The rotary movements are required for coiling of the sliver. On one hand, the rotatable plate must be rotated above the can, while the can itself must rotate, at a considerably slower rate, below the plate. A sliver tube is provided on the plate as a fixed part to guide the sliver from the calendar rollers into the can.



